Actinomyces - Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestation
Pathogenesis of Actinomyces
Actinomyces spp. causes a chronic disease characterized by multiple abscesses and granulomata, tissue destruction, extensive fibrosis, and the formation of sinuses.
Actinomyces spp. is normal floras of the oral cavity, low GI tract, and female genital tract. It causes the company of bacteria for infection or open to cause infection such as Bifidobacterium, Actinobacillus, Bacteroides, Eikenella, Haemophilus, Fusobacterium, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, etc. These bacteria help in the initiation of infection by producing cytotoxins, and enzymes and by inhibiting host immunity.
Once Actinomyces invade the tissue, they develop a chronic granulomatous infection characterized by the formation of tiny clumps known as sulfur granules because of their yellow color, size of granules 0.1-1mm in diameter, and composed of an internal tangle of mycelium filament, and a rosette of peripheral clubs. These granules are stabilized by a protein-polysaccharide complex which provides aid to host defense by inhibiting phagocytosis.
Within diseased tissue, the Actinomyces form large masses of mycelia embedded in an amorphous protein-polysaccharide matrix and surrounded by gram-negative, weakly acid-fast, club-like structures.
Once the infection is established it causes a draining sinus tract which contains, damaged tissue. Then Actinomyces bacteria disseminate by the blood circulation to distant organs. These mycelia masses are visible to the naked eye and are light yellow in color. They are called sulfur granules.
In older lesions, sulfur granules may be dark brown and hardened (due to deposition and calcium phosphate). Actinomyces may colonize diseased tissue, such as lung cancer but sulfur granules are not seen.
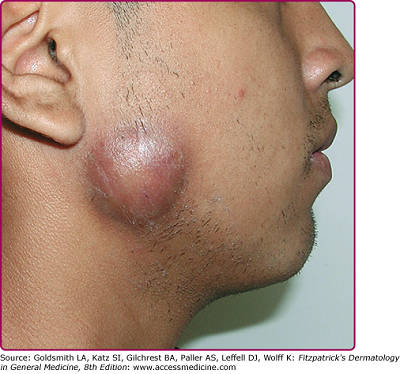
Fig: Cervicofacial actinomycosis (Source: accessmedicine.com)
Clinical Manifestations of Actinomyces
The clinical manifestations of Actinomyces include:
Cervicofacial actinomycosis (1st common)
Thoracic actinomycosis
Abdominal actinomycosis – pulmonary (3rd common)
Pelvic actinomycosis
Bone and joint actinomycosis
Genitourinary actinomycosis (2nd common)
Cervicofacial actinomycosis
In the case of cervicofacial actinomycosis, caused by Actinomyces spp., the jaw is involved and is endogenous in origin. The predisposing factor for this infection is dental carries. Infection may follow tooth extractions or other dental procedures. It causes maxillary osteomyelitis.
Thoracic actinomycosis
Thoracic actinomycosis, caused by Actinomyces spp., occurs in the lungs i.e. pulmonary as a result of aspiration of actinomycosis. Also, it involves endo-bronchial and laryngeal actinomycosis. Sinus appears on the chest wall and ribs as well as the spine may be eroded.
Abdominal actinomycosis
Abdominal actinomycosis, caused by Actinomyces spp., occurs in the appendix or in chronic diverticular.
Pelvic actinomycosis
This type of actinomycosis, caused by Actinomyces spp., occurs mainly in women fitted with plastic intrauterine contraceptive devices.
Bone and joint actinomycosis
Although bone and joint actinomycosis are uncommon, the infection caused by Actinomyces spp. may occur due to an infection in adjacent soft tissue lesions.
Genitourinary actinomycosis
In the case of genitourinary actinomycosis, caused by Actinomyces spp., lymphatics are not usually involved. However, hematogenous spread in the liver, brain and other internal organs may occur.