Astrovirus - Replication, Clinical manifestation, Transmission, Lab Diagnosis, Treatment
Replication of Astrovirus
Astrovirus absorbs into a receptor and is internalized either by endocytosis or direct entry and replication is entirely cytoplasmic.
The astrovirus RNA genome is replicated via a replicative intermediate dsRNA. in addition, a large subgenomic mRNA code for a viral polyprotein, which is cleaved into capsid proteins. New virions self-assemble and may be seen as crystalline arrays in the cytoplasm, hence they are released by cell lysis.
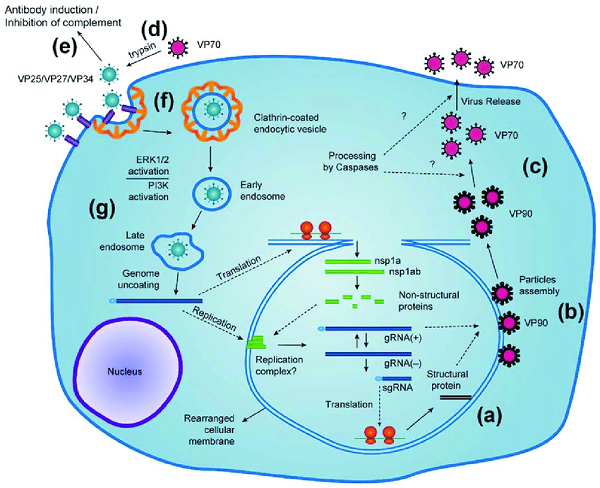
Fig: Astroviruses replication (Source: ResearchGate)
Clinical features/manifestation of Astrovirus
The incubation period of Astrovirus in humans is 3-4 days. The illness lasts for 1-4 days with the excretion of virion particles for up to 2 weeks. In severely immunocompromised cases, persistent excretion of caliciviruses can take place.
The symptoms of astrovirus are mild and rarely require hospital admission. It includes ‘gastric flu’ (i.e. diarrhea, headache, fever, aching limbs, and malaise), projectile vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain, etc. The stool does not contain blood or mucus.
But during outbreaks of Astrovirus among elderly/infant patients with underlying problems, IV rehydration may be necessary. It causes gastroenteritis in children, whose immune systems are underdeveloped and elderly adults whose immune systems are generally somewhat compromised.
Mode of transmission of Astrovirus
The mode of transmission of Astrovirus includes the following routes:
Fecal-oral route
>109 particles per gram
the virus can remain viable for several years
infectious dose: 10-100 particles
Respiratory route
inhalation of aerosols of vomit or fecal material
Foods
It includes cold foods such as sandwiches, iced cakes, melons, and salads.
Seafood that is eaten raw such as Shellfish.
Asymptomatic excretion
Contaminated water
Laboratory diagnosis of Astrovirus
Laboratory diagnosis of Astrovirus is done by following methods
Specimen
Specimen/samples collected for diagnosis of Astrovirus
feces (collected asap and stored at 4°C)
vomitus
contaminated food and drinks
Microscopy
Electron microscopy can be used to demonstrate astrovirus. But they are difficult to recognize. The sensitivity of an electron microscope can be increased by solid-phase immune electron microscopy (IEM) or conventional IEM. IEM is also used to measure Ab responses.
The virus reacts with antibodies in the fluid phase resulting in aggregates of particles. Masking of the virus by antibodies should be prevented.
Serodiagnosis
EIA is one of the serodiagnostic methods available to detect Astrovirus.
Molecular methods
Molecular methods such as RT-PCR have high sensitivity and specificity. Primers to detect Astrovirus are designed to be directed to the highly conserved RNA polymerase region, the VPI region, or the area binding the two regions.
Treatment of Astrovirus
No specific treatment is available for Astrovirus infection while severe dehydration is managed with parenteral fluid replacement.