Treponema pallidum - Clinical manifestation, Venereal Syphilis, Congenital Syphilis
Clinical manifestations
The clinical manifestations of Treponema pallidum include:
Venereal syphilis/Sexually Transmitted Infection
Non-venereal syphilis
Venereal syphilis
In cases of untreated venereal syphilis, caused byTreponema pallidum, characteristic stages include:
incubating
primary syphilis
secondary syphilis
early latent syphilis
latent syphilis
tertiary syphilis
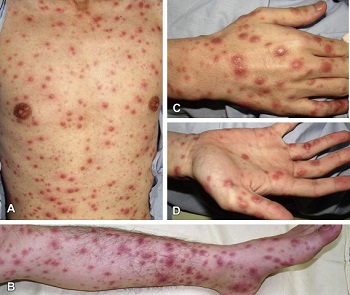
disseminated erythematous papules, nodules with purpuric center on (A) trunk, (B) lower limb, (C) dorsal hands, and (D) palms (Image: Sciencedirect)
Primary syphilis
primary syphilis incubation period of about 3 weeks
In this stage of the disease, the chancre is seen
chancre occurs on the penis/scrotum of 75% of men
chancre occurs on the vulva, cervix, or perineum of more than 50% of women
chancre contains numerous Treponema pallidum and is highly infectious
it heals within 3-6 weeks
Secondary Syphilis
secondary syphilis occurs 2-10 weeks after primary chancre and is most florid 3-4 months after infection
characterized by mucocutaneous lesions which are macular pink to red, discrete, and measure 3-10 mm in diameter
cutaneous lesions may vary from macular to papular, pustular, and nodular type
the lesions are found in the entire body including the palms, soles, and other sites (mostly skin)
this stage is associated with mild symptoms of malaise, weight loss, headache, nausea, fever, pain in the bones, painless generalized lymphadenopathy (85% of patients), and aseptic meningitis may occur
after the secondary phase, the disease caused by Treponema pallidum becomes subclinical but not necessarily dormant (inactive). During this latent phase, diagnosis can be made using serologic methods.
relapses are common during early (<= 1 year) latent syphilis. Late latent syphilis (> 1 year) is usually asymptomatic and non-infectious.
Tertiary syphilis
tertiary syphilis, caused by Treponema pallidum, develops within 3-10 years of infection
gumma is a typical pathological lesion found in the skin, mouth, and the URT
gummatous lesions may be multiple or diffuse but are usually single lesions that measure from 1cm to several cm in diameter
cardiovascular syphilis, eye diseases, chronic granulomatous and meningovascular manifestations, and neurosyphilis are the other manifestations of syphilis, which occur several decades after the infection
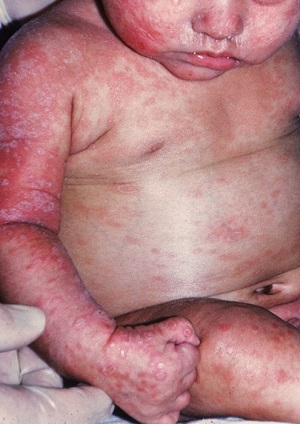
Fig: Congenital syphilis seen on an infant (Source: Ykhoa)
Non-venereal syphilis
The types of non-veneral syphilis caused by Treponema pallidum include:
Congenital syphilis
Occupational syphilis
Congenital syphilis
congenital syphilis occurs by vertical transmission from mother to fetus during pregnancy
in 40% of untreated cases, Treponema pallidum causes late miscarriage, stillbirth, and death.
Occupational syphilis
occupational syphilis, caused by Treponema pallidum, occurs in medical and paramedical workers handling cases of secondary syphilis
the lesion usually develops on the palm and other exposed body parts