Treponema pallidum - Lab diagnosis, Microscopy, Serodiagnosis, Culture
Laboratory diagnosis of Treponema pallidum
The laboratory diagnosis of Treponema pallidum begins with the collection of samples:
Specimen collection
serum, serous fluid, CSF (in case of neurosyphilis)
a small section of the umbilical cord (for congenital syphilis)
tissue/needle aspirated of lymph nodes
Microscopy
Treponema pallidum is too thin to be seen microscopically by performing Gram staining or Giemsa staining. This is stained by the silver impregnation method.
Levaditis method and Fontana’s methods are types of silver impregnation methods that are to stain tissue sections and blood films respectively
Darkfield microscopy
viewed as motile, long (8-10 μm) with 8-14 tightly coils even spirals can be observed at 400x high-dry magnification
helpful for early diagnosis before the appearance of antibiotics
if the initial test is negative, the procedure should be repeated daily for at least 3 days because the commensal spirochete might interfere with microscopy
saprophytic non-pathogenic Treponemas are present as normal flora in the oropharynx.
the limitation of this procedure is that it can be only examined by experienced microscopists and it has low sensitivity.
(At least 104 CFU/ml must be present in exudates)
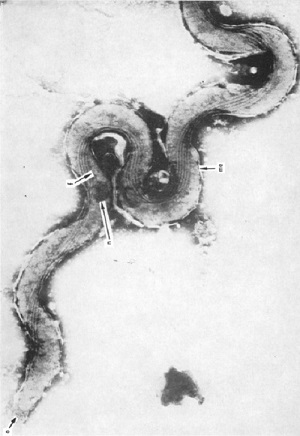
Image: ultra-thin segments of Treponema pallidum viewed by electron microscope (Delektorskij, V. V.;Ovčinnikov N. M., 1966)
Direct Antigen detection
Treponema pallidum antigen can be detected in the sample after the use of direct antigen such as a fluorescent antibody test.
Fluorescent antibody testing
the specimen is taken in a clean grease-free slide, air-dried, and fixed with acetone. Fluorescein-labeled monoclonal antibody for Antigen on Treponema pallidum is used and observed under the fluorescent microscope.
- this test has 85-92% sensitive
Serodiagnosis
Serodiagnosis methods measure two types of antibodies produced against Treponema pallidum.
treponemal (are produced against Ag of organisms itself)
non-treponemal / reagin antibodies (are produced in infected patients against components of mammalian cells and are produced in other diseases including leprosy, malaria, and measles.
Treponema pallidum haemagglutination assay (TPHA)
Cardiolipin Ag test / Rapid Plasma Reagin test (RPR test)
Venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL)
VDRL and RPR tests are non-treponemal serological tests
specific treponemal serological tests include EIA and agglutination tests such as:
Treponema pallidum particle agglutination (TP-PA)
microhemagglutination assay (MHA-TP)
Treponema pallidum indirect hamagglutination (TPHA)
Treponema pallidum immobilization test
Particle gel immunoassay (PaGIA)
Fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption (FTA-ABS) test
Molecular diagnosis
Molecular diagnosis such as PCR can be used for the detection of Treponema pallidum within exudate/lesions
Culture
Treponema pallidum are microaerophilic
Unlike other microorganisms, they do not grow in artificial culture media. They have, however, been maintained for a long time by subcultures in animals.
strains of Treponema pallidum can be and have been maintained for a short period of time in cell lines including Eagle and McCoy cell lines which have been supplemented with fetal bovine serum as well as a reducing agent.
These spirochaetes can be stored in a medium containing 5% glycerol at 70°C (158°F) or liquid nitrogen at -130°C (-202°F) for 10 to 15 years.
AST (antibiotic susceptibility test) cannot be performed as culture in media has not been possible.
Western blot
Western blot confirmatory test but is not used in routine confirmation
high specificity and sensitivity
Other properties
It is easily killed by drying or heating at 41-42°C(105.8°F – 106,8°F)for 60 minutes at 0-4°C for 1-3 days.
also killed on contact with distilled water, soap, arsenic compounds, mercuric compounds, bismuth compounds, and common antiseptics.
Infection of Treponema pallidum produces at least three types of antibodies against
Cardiolipin antigen
Treponema pallidum group-specific antigen
Treponema pallidum species-specific antigen